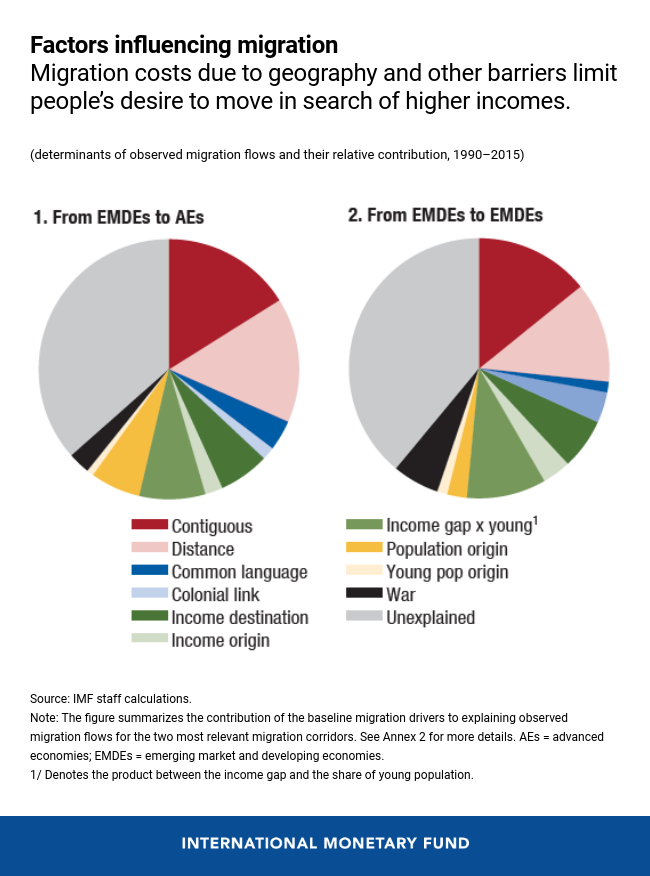
Migration is an important part of the globalized world we live in today. It has the potential to bring great economic benefits to both the sending and receiving countries. However, there are also potential risks and drawbacks to the movement of people across borders. This article explores the effects of migration on economies, both positive and negative, to help readers better understand the complexities of this issue.
Migration Impact on Regional Economics
Migration has long been a significant factor in the global economy, and its impact can be seen at a regional level as well. Migration has far-reaching implications for regional economics, affecting everything from labor markets to housing to public services.
One of the most evident impacts of migration on regional economics is the effect on labor markets. Migration can provide a regional economy with an influx of both skilled and unskilled labor, allowing businesses to access a larger pool of talent. This influx of new workers can also help to offset labor shortages in certain industries, allowing economic activity to continue.
Migration can also have an effect on housing markets. Migration can create increased demand for housing in certain areas, which can lead to higher prices, or can create a housing shortage in areas with a large influx of migrants. This can have a significant impact on the local economy, as residents may have to pay more for housing or may be unable to find suitable housing.
Finally, migration can also have an impact on public services. As more migrants enter a region, there is an increased demand for services such as health care, education, and transportation. This can lead to an increased strain on public services, leading to higher taxes and increased costs for local governments.
In summary, migration has a significant impact on regional economics. Migration can provide an influx of labor, affect housing markets, and place an increased strain on public services. It is important for governments to consider the potential impacts of migration on regional economics when developing policies.
Migration & Economic Status
Migration is the process of moving from one area to another, either within a country or internationally. Migration can be voluntary or involuntary, with people relocating for a variety of reasons including political, economic, environmental, and social. Migration can have a significant impact on an individual’s economic status.
When people migrate for economic reasons, it is often for the purpose of seeking higher wages or better job opportunities. People in developing countries often move to developed countries in search of work, with the hope of improving their economic status. This type of migration can be beneficial for both the migrants and the host countries, as migrants are able to improve their economic situation and the host countries can benefit from increased economic activity and increased labor supply.
Migration can also have a negative impact on economic status. Migrants often leave behind family members and friends, and may face language and cultural barriers in their new location. This can lead to feelings of isolation and difficulty in finding employment, leading to a decrease in economic status. Additionally, migrants can often be subject to exploitation and abuse, which can further reduce their economic status.
Finally, migration can also affect economic status indirectly. Migration can lead to an increase in the number of people in a given area, which can lead to increased competition for jobs and resources. This can lead to increased economic disparities, as those with more resources are often more able to compete for jobs and resources. Additionally, migration can also lead to increased demand for housing and other services, driving up prices and making it more difficult for people to afford basic necessities.
In summary, migration can have both positive and negative impacts on economic status. For some, migration can lead to improved economic opportunities and higher wages. For others, migration can lead to decreased economic status due to language and cultural barriers, exploitation, and increased competition for jobs and resources. Regardless of the outcome, it is important to consider the potential economic implications of migration.
Economic & Social Consequences of Migration
Migration has been an integral part of human history, and it has had both economic and social consequences. Migration can be defined as the movement of people from one place to another, and can be either voluntary or forced. It can involve movement within a country, or across borders.
The economic consequences of migration depend on the type of migration that is occurring. Migration can have a positive or negative economic effect, depending on the level of skills of the migrants and the labor market demand for those skills in the new location. Skilled migrants can contribute to the economic development of the receiving country by bringing in new skills and labor that can increase productivity and help to create jobs. Unskilled migrants can put a strain on the welfare systems of receiving countries, as they may not have the skills or resources to contribute to the economy.
Migration can also lead to social consequences. Migration can lead to cultural integration and assimilation, as migrants bring their culture and values to the receiving country. This can lead to positive outcomes such as greater cultural understanding and tolerance, but it can also lead to negative outcomes such as language barriers and social exclusion. Migration can also cause social tensions, as some people may view migrants as a threat to their culture and livelihoods.
In conclusion, migration can have both economic and social consequences. The effects of migration depend on the type of migration and the skills and resources of the migrants. In some cases, migration can have positive outcomes, such as increased economic productivity and cultural integration, but it can also lead to negative outcomes such as social exclusion and tension.
Effects of Migration on Country
Migration is the movement of people from one location to another, and this phenomenon can have a variety of effects on a country. Migration can have positive and negative impacts on a country’s economy, society, and culture.
The economic effects of migration can be both positive and negative. On the positive side, migrants may bring with them valuable skills or capital that can help to stimulate the economy. For example, skilled migrants may provide a boost to a country’s labor market, allowing businesses to access a larger pool of qualified employees. In addition, migrants may bring with them a desire to invest, providing capital to help drive economic growth. On the negative side, however, migrants may compete with local workers for jobs, causing wages to decrease and leading to increased unemployment. Additionally, migrants may strain the country’s welfare system, as they may be more likely to use public services than native-born citizens.
Migration can also have effects on a country’s society and culture. On the positive side, migrants may bring with them a variety of cultural perspectives and experiences, which can enrich the country’s culture. In addition, migrants may also make valuable contributions to their new country, such as volunteering in their communities or working in low-paying jobs that could otherwise go unfilled. On the negative side, however, migration can lead to tension between migrants and native-born citizens, as well as between different racial or ethnic groups of migrants.
In conclusion, migration can have both positive and negative effects on a country’s economy, society, and culture. While migrants may bring valuable skills and capital, they may also put strain on the country’s welfare system and cause tension between different groups. It is important for countries to carefully consider the potential impacts of migration before allowing large numbers of people to move into their countries.
In conclusion, migration can bring both positive and negative consequences to an economy. On one hand, migration can provide a country with a larger and more diverse pool of skilled labor and increased consumer demand, while on the other hand, it can lead to wage stagnation, increased competition for jobs, and the potential for social unrest. Despite the complexities and potential risks of migration, it can be a powerful and beneficial tool for economic growth and development when managed and regulated effectively.
